Protects the Internal Tissues of the Body From Potential Harm
Immune System defends the body after it has been invaded by a microscopic organism. Tissues that work together to perform a specific bodily function.
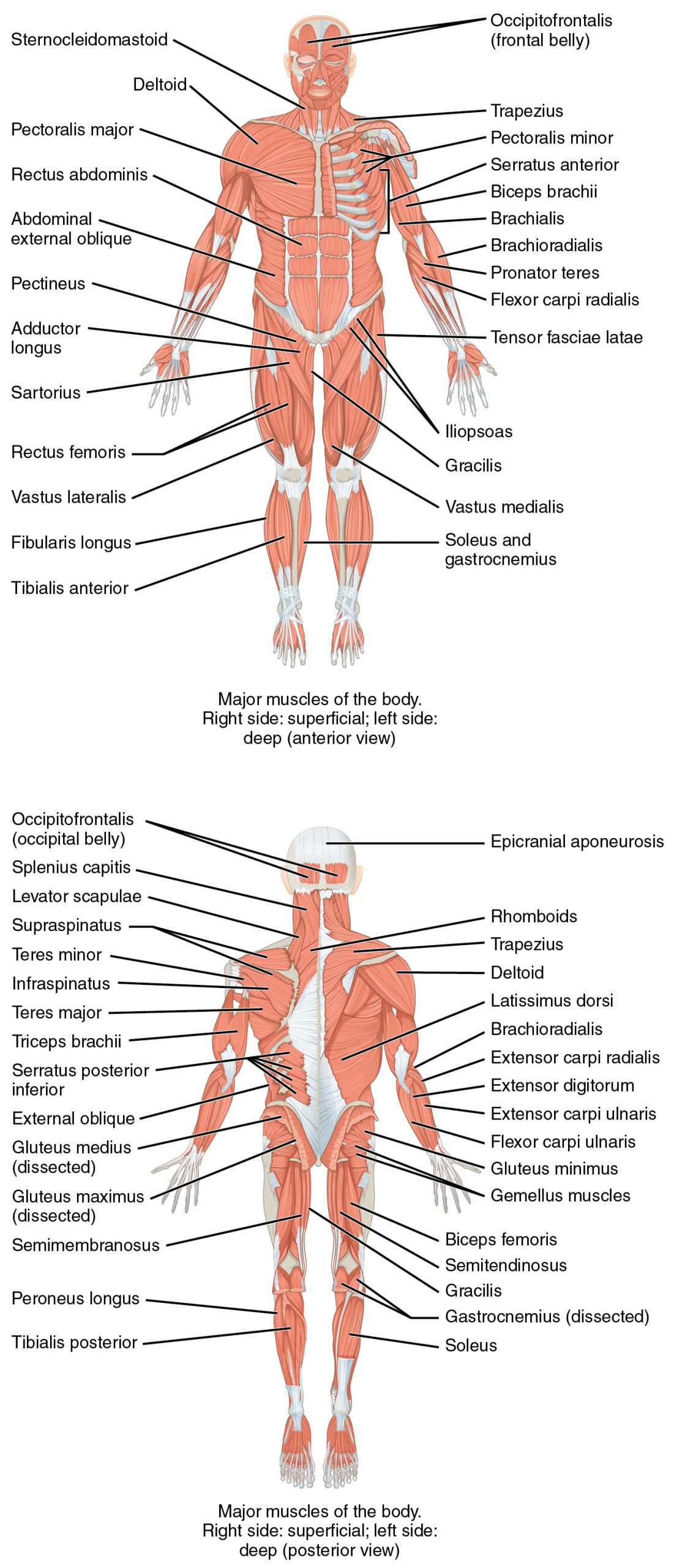
Muscular System Building A Medical Terminology Foundation
___ membranes protect the internal organs from friction and hold them in place.

. The Four Basic Tissue Types of the Human Body. EPITHELIUM EPITHELIAL TISSUE Functions jobs. Passage of substances from a body system into the circulatory system Filtration.
Basic structural unit of the body 5. Epithelial tissue protects several aspects of your body. Integumentary System protects the internal tissues of the body from potential harm.
There are four main tissues in the body epithelium muscle connective tissue and nervous tissue. The sievert Sv is the unit of effective dose that takes into account the type of radiation and sensitivity of tissues and organs. Defends the body after it has been invaded by a microscopic organism.
Two examples of how internal body tissues are protected are. Defends the body after it has been invaded by a microscopic organism. Regulates the bodys metabolism growth and functions of the sexual organs.
Inflammation in the liver protects this organ from infection and injury but excessive inflammation may lead to extensive loss of hepatocytes ischemia-reperfusion injury metabolic alterations and eventually permanent hepatic damage. The distinctive appearance of cartilage is due to polysaccharides called chondroitin sulfates which bind with ground substance proteins to. Defends your body from any organisms that threaten the destruction of cells 2.
Two major forms of supportive connective tissue cartilage and bone allow the body to maintain its posture and protect internal organs. Responsible for the conception of new life. Regulates the bodys metabolism growth and functions of the sexual organs.
White blood cells that produce antibodies 3. The skin protects tissues from invasion of harmful external substances. System of vessels that are responsible for the removal of bacteria from the bloodstream 4.
Inflammation can destroy hepatic parenchymal cells increasing the risk of chronic liver diseases such as non-alcoholic. The integumentary system protects the bodys internal living tissues and organs protects against invasion by infectious organism and protects the body from dehydration. Defends the body after it has been invaded by a microscopic organism.
Protects the internal tissues of the body from potential harm. Defends the body after it has been invaded by a microscopic organism. All of the above.
Protects the body from physical damage. Internal communication Muscle tissue. It protects us from the outside world skin.
____ membranes line digestive respiratory excretory and reproductive passages. Protects the internal tissues of the body from. The immune system is a vast and complex interconnected network of many different organs cells and proteins that work together to protect the body from illness.
An important vitamin synthesized thanks to the skin. Understanding how the immune system. Regulates the bodys metabolism growth and functions of the sexual organs.
System works with the circulatory system to add oxygen to the blood and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Two major forms of supportive connective tissue cartilage and bone allow the body to maintain its posture and protect internal organs. Defends the body after it has been invaded by a microscopic organism.
It is a way to measure ionizing radiation in terms of the potential for causing harm. Cells that help protect our body from radiological damage. The cilia on the epithelial cells that line your intestines protect the rest of your body from intestinal bacteria.
The distinctive appearance of cartilage is due to polysaccharides called chondroitin sulfates which bind with ground substance proteins to. Most epithelial tissues have one free or ___ surface and a ___ surface that is attached to a basement membrane. Protects the internal tissues of the body from potential harm.
Determine which vessels leave enter the body. Protects the internal tissues of the body from potential harm. Insulates body Cushions and protects internal organs.
For example your skin is made up of epithelial tissue and protects the tissues deeper in your body such as blood vessels muscle and internal organs. Human body has seven main systems which perform specific functions. Regulates the bodys metabolism growth and functions of the sexual organs.
Protects the internal tissues of the body from potential harm. A healthy immune system can defeat invading disease-causing germs or pathogens such as bacteria viruses parasitesas well as cancer cellswhile protecting healthy tissue. Regulates the bodys metabolism growth and the functions of the sexual organs integumentary system protects the internal tissues of the body from potential harm responsible for the conception of new life.
The effective dose is used to measure ionizing radiation in terms of the potential for causing harm. Contracts to cause movement. Passage of substances through a membrane or filter.
Protects the internal tissues of the body from potential harm. Endocrine System regulates the bodys metabolism growth and functions of the sexual organs. Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure form and function job.
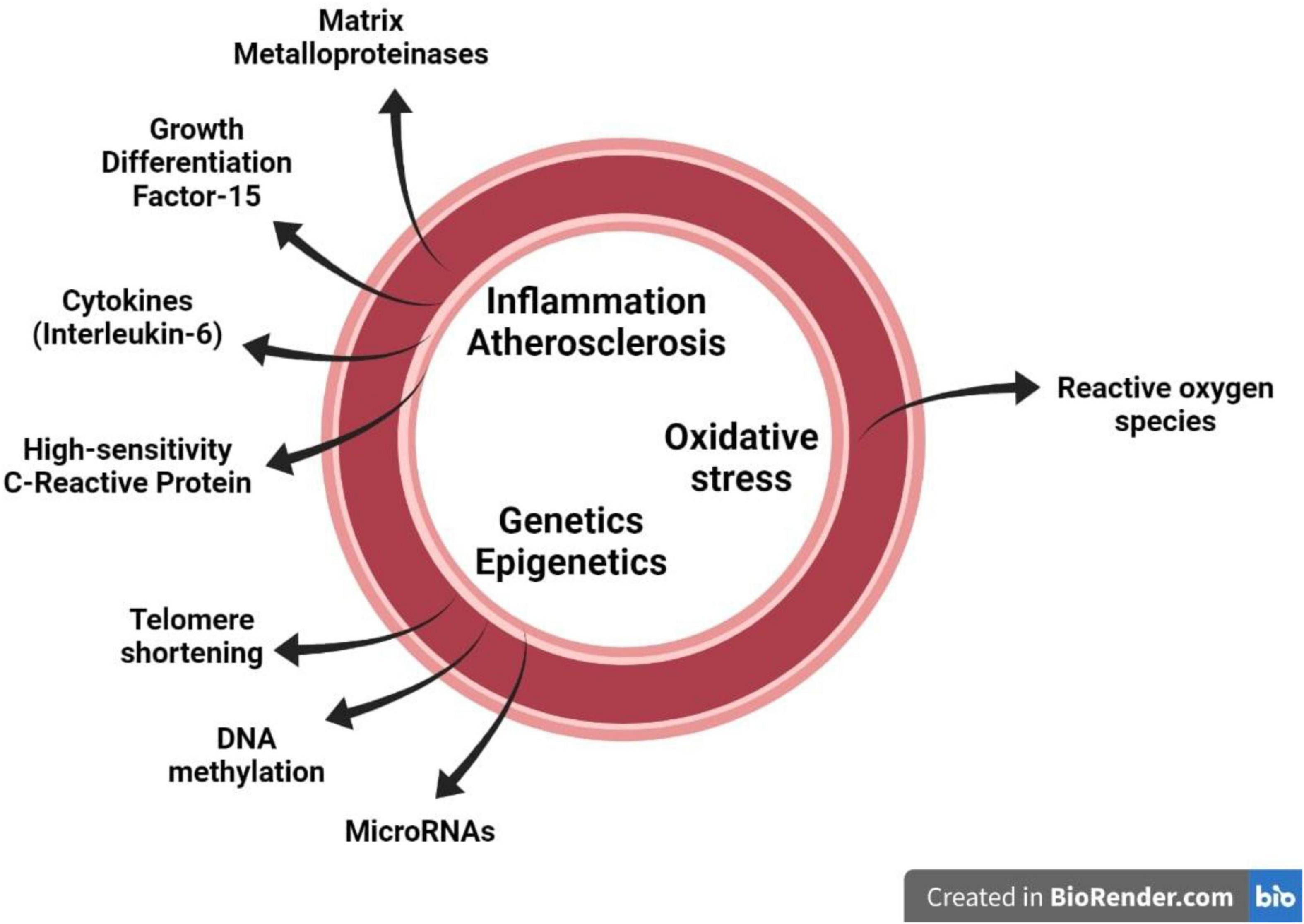
Frontiers Pathophysiology Of Circulating Biomarkers And Relationship With Vascular Aging A Review Of The Literature From Vascagenet Group On Circulating Biomarkers European Cooperation In Science And Technology Action 18216 Physiology
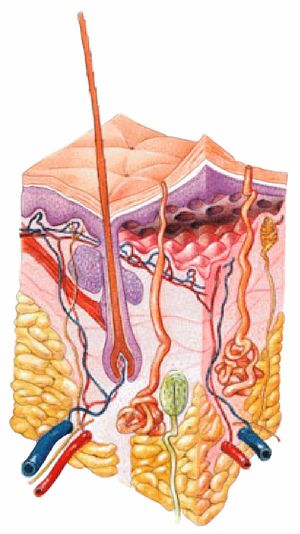
Integumentary System Physiopedia

Wound Healing And The Immune System Science In The News
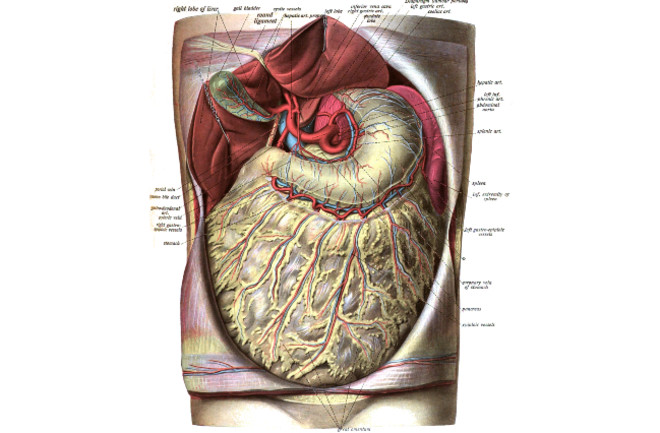
The Omentum A Curtain Of Tissue That Keeps Our Guts Working Discover Magazine
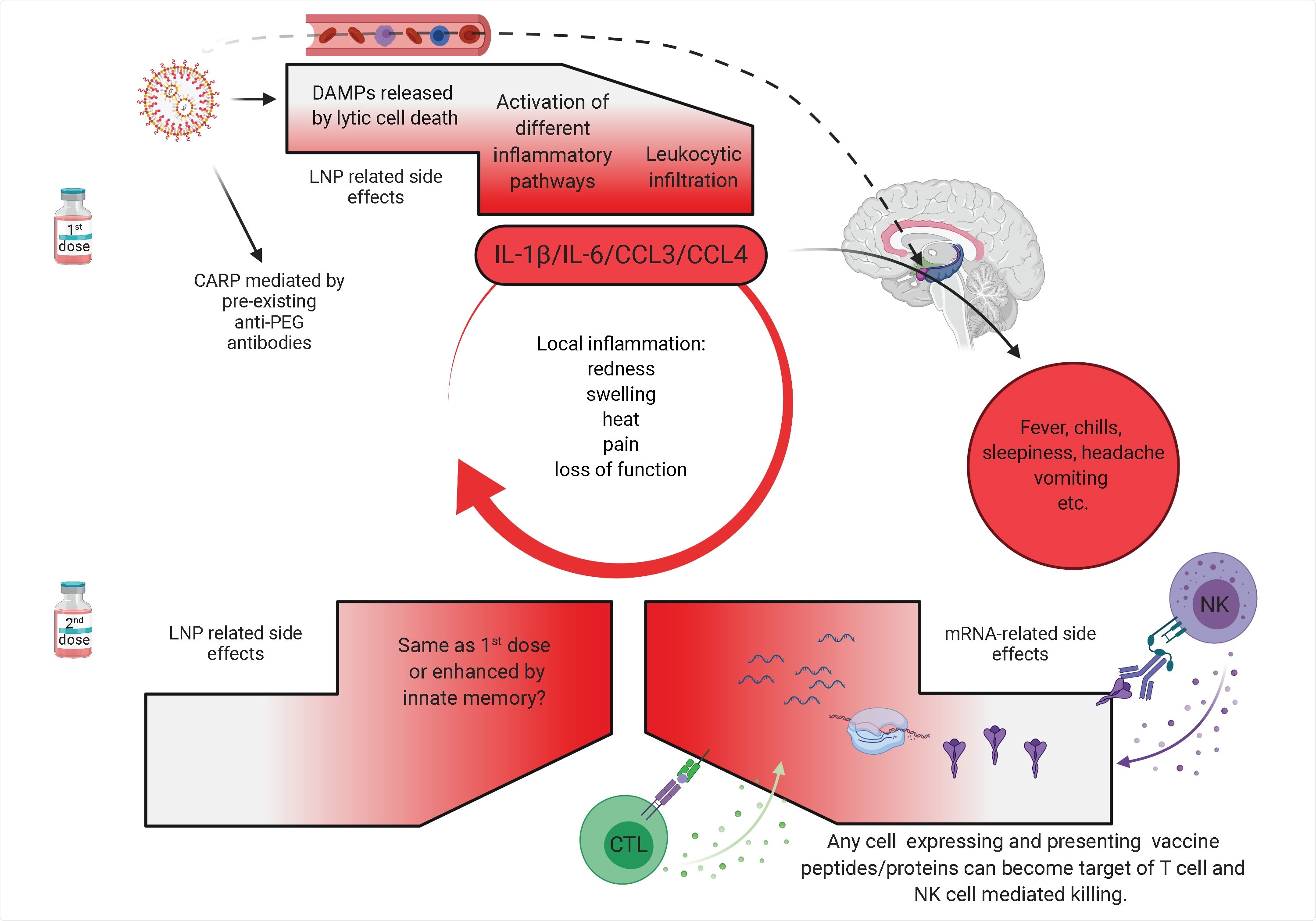
Research Looks At Inflammatory Nature Of Lipid Nanoparticle Component In Mrna Vaccines

17 Questions About Health And Wellness Answered Britannica
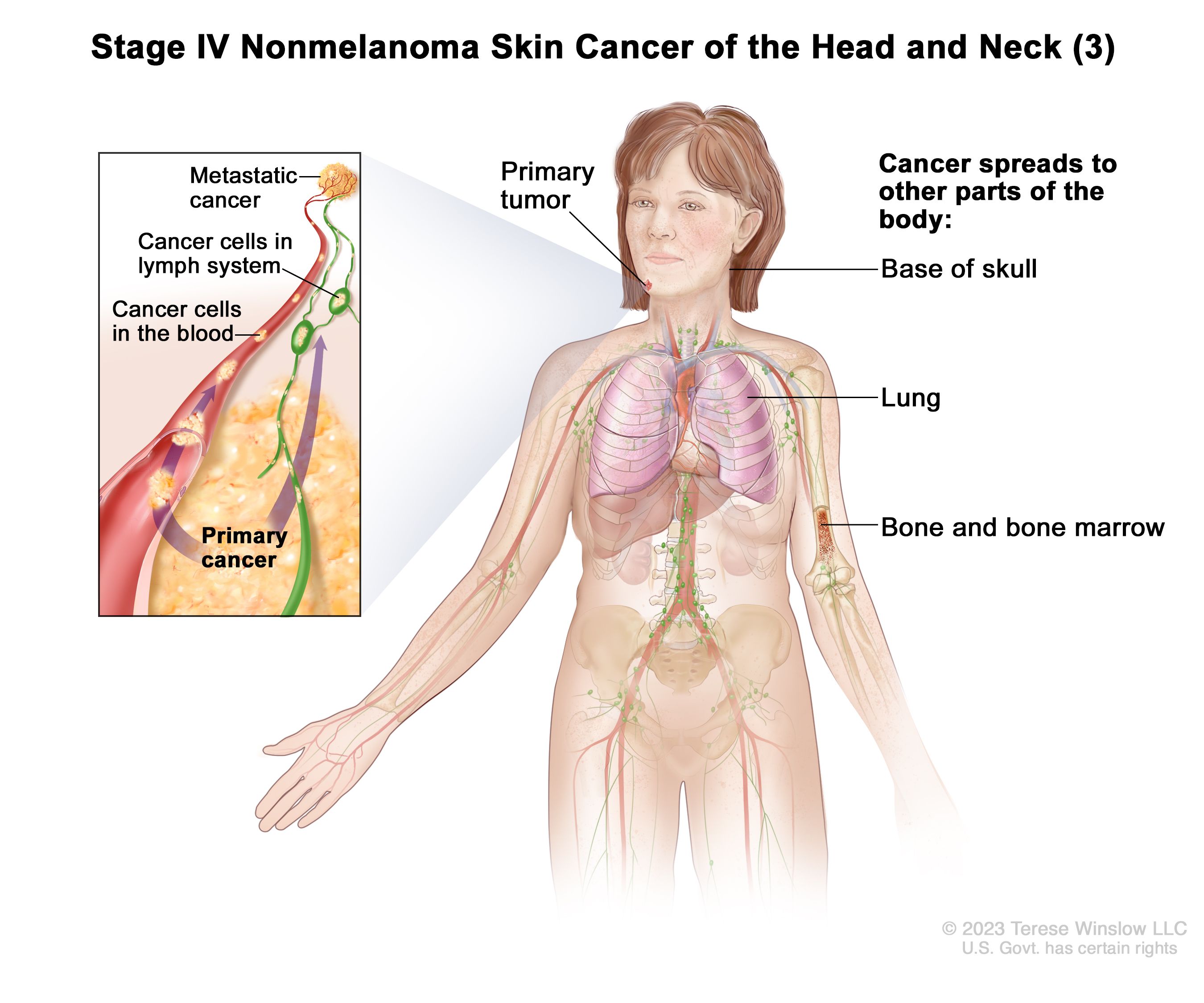
Skin Cancer Types Symptoms Information Dana Farber Cancer Institute Boston Ma
/Bodysystems-ef5a7b1697e3483a9cba9c5aafc4c75d.jpg)
Rheumatoid Arthritis Effects On The Body Systems
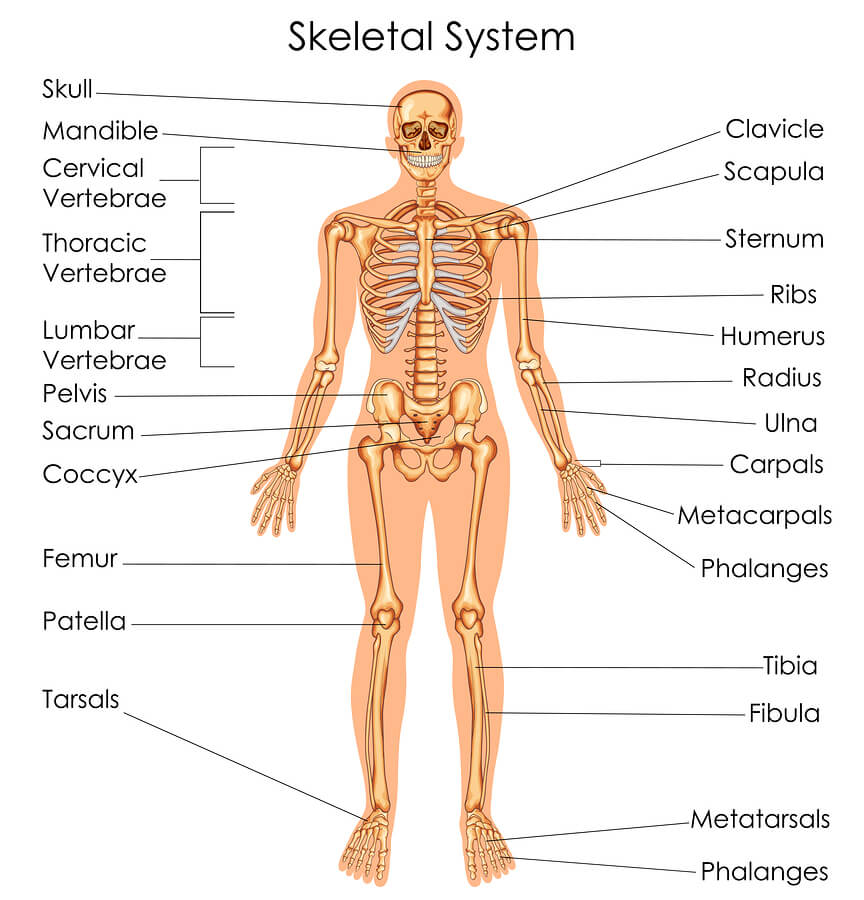
How Drugs Alcohol Affect The Skeletal System
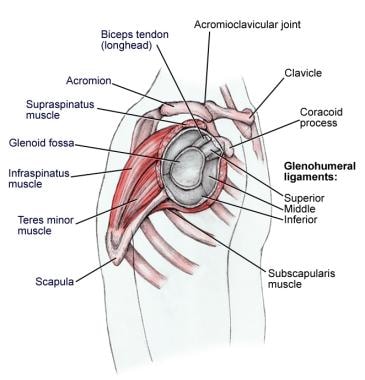
Shoulder Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy

The Lymphatic System 2 Structure And Function Of The Lymphoid Organs Nursing Times
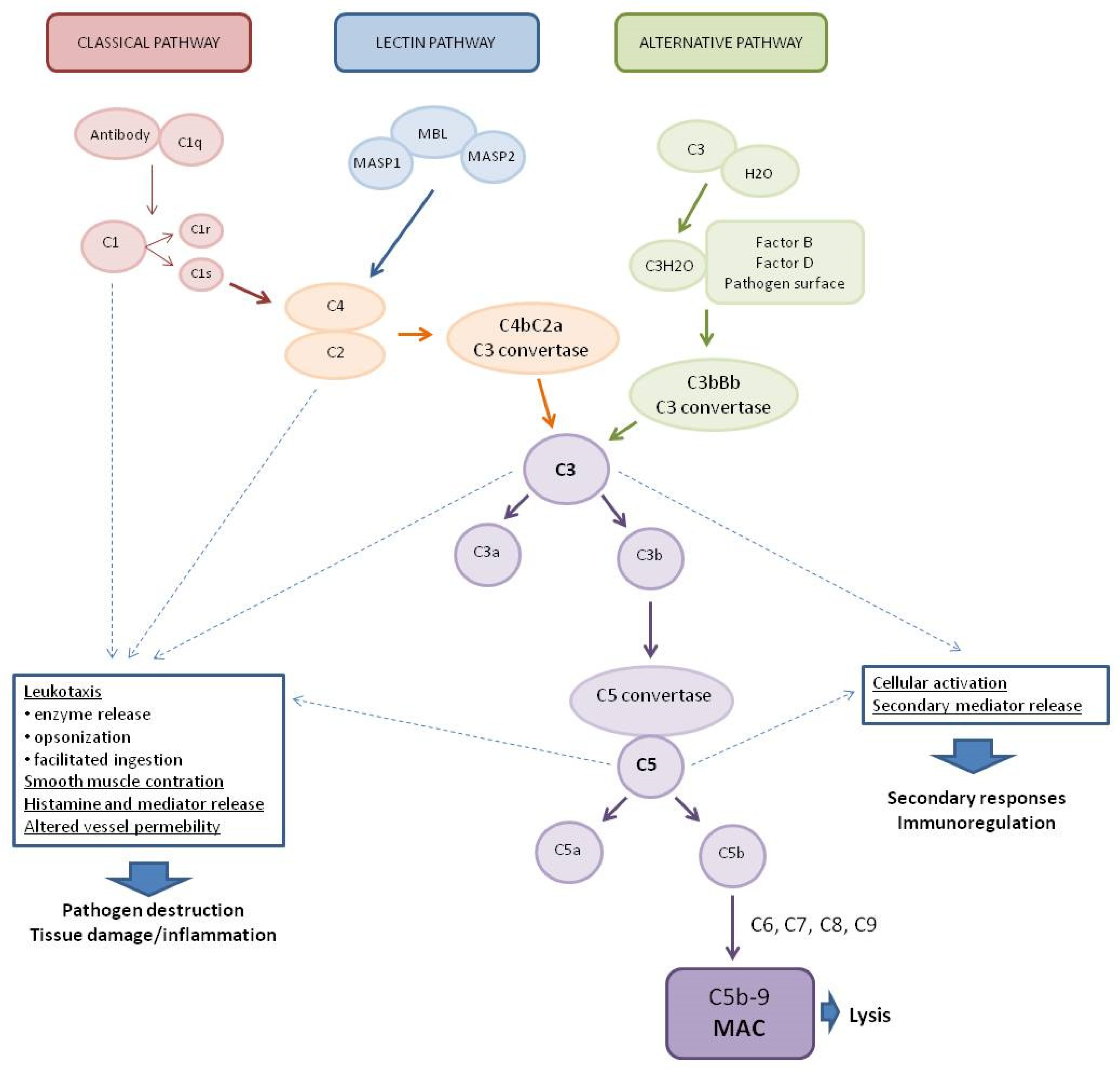
Biomolecules Free Full Text New Insights Into The Role Of The Complement System In Human Viral Diseases Html
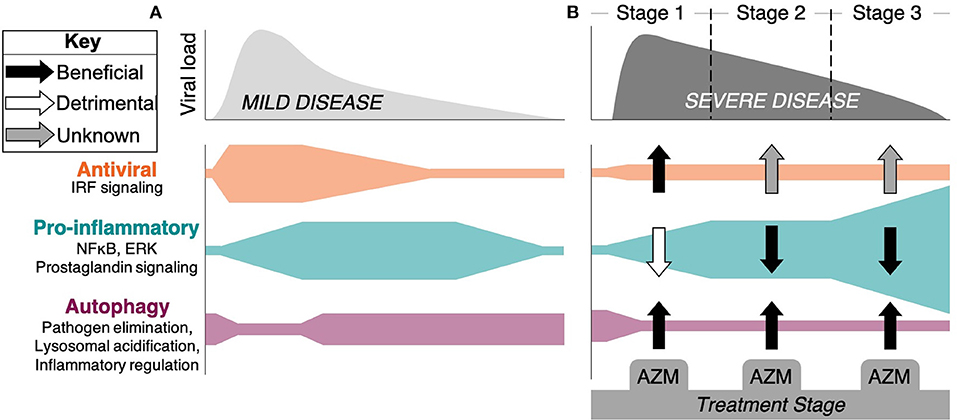
Frontiers Immunomodulatory Effects Of Azithromycin Revisited Potential Applications To Covid 19 Immunology
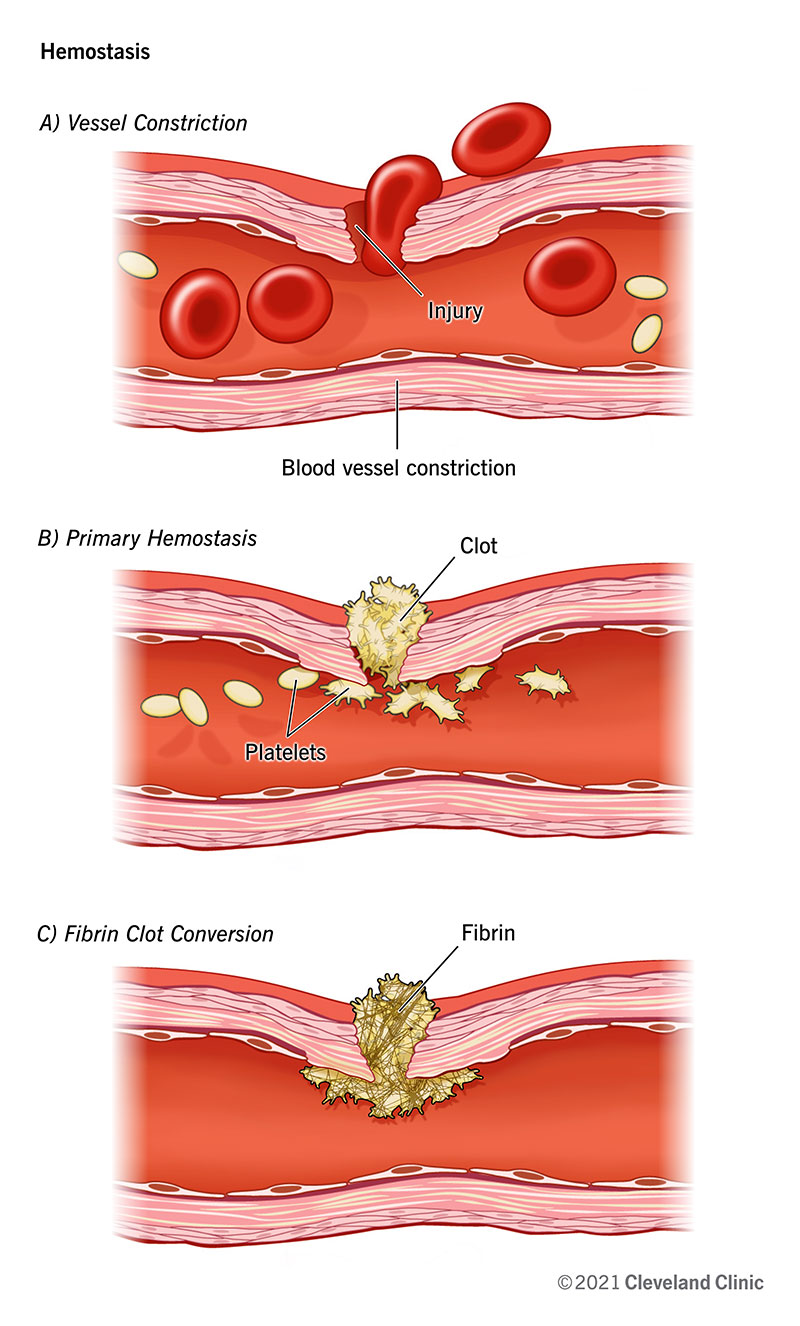
Hemostasis Stages And How The Process Stops Blood Flow
The Potential Role Of Sleep In Promoting A Healthy Body Composition Underlying Mechanisms Determining Muscle Fat And Bone Mass And Their Association With Sleep Fulltext Neuroendocrinology Karger Publishers
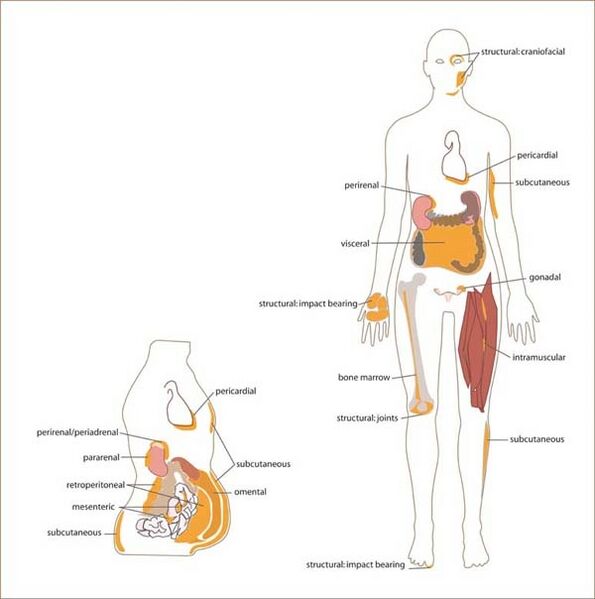

Comments
Post a Comment